By Now You should know your Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) and have calculated or Caloric needs for the day.
Your assignment is to create two very different menus.
One menu should consist of the types of food that is consumed often by your age group and considered unhealthy. You must determine the total calories for the food consumed find the total value of the food and the total Grams of Fat as well.
The second menu has the same objective but it will be an entirely different menu. You are challenged to develop this menu with only nutritious, healthy options. However, they must be foods that you would actually eat. For example, If you would not eat cucumbers....do not have a tomato and cucumber salad on your menu.
This Assignment is due on Tuesday Nov. 12
Sunday 10 November 2013
Friday 11 October 2013
Tuesday 10 September 2013
Fitness Testing Reflection
Mr. Thomson's PPL2OM Students (gr. 10 boys Gym Class)
I would like you to reply or comment on this post with a reflection on your fitness testing. You do not have to comment on your specific data, but rather, I would like to see your plans on how you can improve or maintain your fitness to have better results at the conclusion of the semester.
Your post should be 100-200 words in length.
Topics you post can or should include...
I would like you to reply or comment on this post with a reflection on your fitness testing. You do not have to comment on your specific data, but rather, I would like to see your plans on how you can improve or maintain your fitness to have better results at the conclusion of the semester.
Your post should be 100-200 words in length.
Topics you post can or should include...
- Reflection on your recent fitness tests
- your current level of personal fitness
- strategies to improve
- goals for the semester
All post should be submitted before 11:59 pm Sunday Sept. 15
Monday 19 August 2013
Self Defense
Many people think of self-defense as a karate kick to the groin or jab in the eyes of an attacker. But self-defense actually means doing everything possible to avoid fighting someone who threatens or attacks you. Self-defense is all about using your smarts — not your fists.
Use Your Head
People (guys as well as girls) who are threatened and fight back "in self-defense" actually risk making a situation worse. The attacker, who is already edgy and pumped up on adrenaline — and who knows what else — may become even more angry and violent. The best way to handle any attack or threat of attack is to try to get away. This way, you're least likely to be injured.
One way to avoid a potential attack before it happens is to trust your instincts. Your intuition, combined with your common sense, can help get you out of trouble. For example, if you're running alone on the school track and you suddenly feel like you're being watched, that could be your intuition telling you something. Your common sense would then tell you that it's a good idea to get back to where there are more people around.
De-Escalating a Bad Situation

Attackers aren't always strangers who jump out of dark alleys. Sadly, teens can be attacked by people they know. That's where another important self-defense skill comes into play. This skill is something self-defense experts and negotiators call de-escalation.
De-escalating a situation means speaking or acting in a way that can prevent things from getting worse. The classic example of de-escalation is giving a robber your money rather than trying to fight or run. But de-escalation can work in other ways, too. For example, if someone harasses you when there's no one else around, you can de-escalate things by agreeing with him or her. You don't have to actually believe the taunts, of course, you're just using words to get you out of a tight spot. Then you can redirect the bully's focus ("Oops, I just heard the bell for third period"), and calmly walk away from the situation.
Something as simple as not losing your temper can de-escalate a situation. Learn how to manage your own anger effectively so that you can talk or walk away without using your fists or weapons.
Although de-escalation won't always work, it can only help matters if you remain calm and don't give the would-be attacker any extra ammunition. Whether it's a stranger or someone you thought you could trust, saying and doing things that don't threaten your attacker can give you some control.
Reduce Your Risks
Another part of self-defense is doing things that can help you stay safe. Here are some tips from the National Crime Prevention Council and other experts:
- Understand your surroundings. Walk or hang out in areas that are open, well lit, and well traveled. Become familiar with the buildings, parking lots, parks, and other places you walk. Pay particular attention to places where someone could hide — such as stairways and bushes.
- Avoid shortcuts that take you through isolated areas.
- If you're going out at night, travel in a group.
- Make sure your friends and parents know your daily schedule (classes, sports practice, club meetings, etc.). If you go on a date or with friends for an after-game snack, let someone know where you're going and when you expect to return.
- Check out hangouts. Do they look safe? Are you comfortable being there? Ask yourself if the people around you seem to share your views on fun activities — if you think they're being reckless, move on.
- Be sure your body language shows a sense of confidence. Look like you know where you're going and act alert.
- When riding on public transportation, sit near the driver and stay awake. Attackers are looking for vulnerable targets.
- Carry a cell phone if possible. Make sure it's programmed with your parents' phone number.
- Be willing to report crimes in your neighborhood and school to the police.
Take a Self-Defense Class
The best way — in fact the only way — to prepare yourself to fight off an attacker is to take a self-defense class. We'd love to give you all the right moves in an article, but some things you just have to learn in person.
A good self-defense class can teach you how to size up a situation and decide what you should do. Self-defense classes can also teach special techniques for breaking an attacker's grasp and other things you can do to get away. For example, attackers usually anticipate how their victim might react — that kick to the groin or jab to the eyes, for instance. A good self-defense class can teach you ways to surprise your attacker and catch him or her off guard.

One of the best things people take away from self-defense classes is self-confidence. The last thing you want to be thinking about during an attack is, "Can I really pull this self-defense tactic off?" It's much easier to take action in an emergency if you've already had a few dry runs.
A self-defense class should give you a chance to practice your moves. If you take a class with a friend, you can continue practicing on each other to keep the moves fresh in your mind long after the class is over.
Check out your local YMCA, community hospital, or community center for classes. If they don't have them, they may be able to tell you who does. Your PE teacher or school counselor may also be a great resource.
Basketball
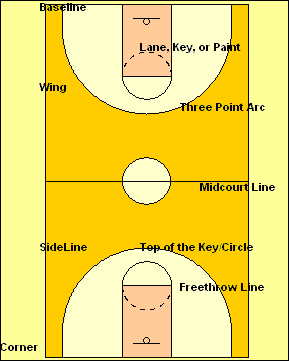
Basketball Court 1
The ball is moved down the court toward the basket by passing or dribbling. The team with the ball is called the offense. The team without the ball is called the defense. They try to steal the ball, contest shots, steal and deflect passes, and garner rebounds.
When a team makes a basket, they score two points and the ball goes to the other team. If a basket, or field goal, is made outside of the three-point arc, then that basket is worth three points. A free throw is worth one point. Free throws are awarded to a team according to some formats involving the number of fouls committed in a half and/or the type of foul committed. Fouling a shooter always results in two or three free throws being awarded the shooter, depending upon where he was when he shot. If he was beyond the three-point line, then he gets three shots. Other types of fouls do not result in free throws being awarded until a certain number have accumulated during a half. Once that number is reached, then the player who was fouled is awarded a '1-and-1' opportunity. If he makes his first free throw, he gets to attempt a second. If he misses the first shot, the ball is live on the rebound.
Each game is divided into sections. All levels have two halves. In college, each half is twenty minutes long. In high school and below, the halves are divided into eight (and sometimes, six) minute quarters. In the pros, quarters are twelve minutes long. There is a gap of several minutes between halves. Gaps between quarters are relatively short. If the score is tied at the end of regulation, then overtime periods of various lengths are played until a winner emerges.
Each team is assigned a basket or goal to defend. This means that the other basket is their scoring basket. At halftime, the teams switch goals. The game begins with one player from either team at center court. A referee will toss the ball up between the two. The player that gets his hands on the ball will tip it to a teammate. This is called a tip-off. In addition to stealing the ball from an opposing player, there are other ways for a team to get the ball.
One such way is if the other team commits a foul or violation.
FOULS
Personal fouls include any type of illegal physical contact.
Blocking. Blocking is illegal personal contact resulting from a defender not establishing position in time to prevent an opponent's drive to the basket.
Flagrant foul. Violent contact with an opponent. This includes hitting, kicking, and punching. This type of foul results in free throws plus the offense retaining possession of the ball after the free throws.
Intentional foul. When a player makes physical contact with another player with no reasonable effort to steal the ball. It is a judgment call for the officials.
Technical foul. Technical foul. A player or a coach can commit this type of foul. It does not involve player contact or the ball but is instead about the 'manners' of the game. Foul language, obscenity, obscene gestures, and even arguing can be considered a technical foul, as can technical details regarding filling in the scorebook improperly or dunking during warm-ups.
VIOLATIONS
Walking/Traveling. Taking more than 'a step and a half' without dribbling the ball is traveling. Moving your pivot foot once you've stopped dribbling is traveling.
Carrying/palming. When a player dribbles the ball with his hand too far to the side of or, sometimes, even under the ball.
Double Dribble. Dribbling the ball with both hands on the ball at the same time or picking up the dribble and then dribbling again is a double dribble.
Held ball. Occasionally, two or more opposing players will gain possession of the ball at the same time. In order to avoid a prolonged and/or violent tussle, the referee stops the action and awards the ball to one team or the other on a rotating basis.
Goaltending. If a defensive player interferes with a shot while it's on the way down toward the basket, while it's on the way up toward the basket after having touched the backboard, or while it's in the cylinder above the rim, it's goaltending and the shot counts. If committed by an offensive player, it's a violation and the ball is awarded to the opposing team for a throw-in.
Backcourt violation. Once the offense has brought the ball across the mid-court line, they cannot go back across the line during possession. If they do, the ball is awarded to the other team to pass inbounds.
Time restrictions. A player passing the ball inbounds has five seconds to pass the ball. If he does not, then the ball is awarded to the other team. Other time restrictions include the rule that a player cannot have the ball for more than five seconds when being closely guarded and, in some states and levels, shot-clock restrictions requiring a team to attempt a shot within a given time frame.
Offensive -- The center's goal is to get open for a pass and to shoot. They are also responsible for blocking defenders, known as picking or screening, to open other players up for driving to the basket for a goal. Centers are expected to get some offensive rebounds and put-backs.
Defensive -- On defense, the center's main responsibility is to keep opponents from shooting by blocking shots and passes in the key area. They also are expected to get a lot of rebounds because they're taller.
Forward. Your next tallest players will most likely be your forwards. While a forward may be called upon to play under the hoop, they may also be required to operate in the wings and corner areas.
Offensive -- Forwards are responsible to get free for a pass, take outside shots, drive for goals, and rebound.
Defensive -- Responsibilities include preventing drives to the goal and rebounding.
Guard. These are potentially your shortest players and they should be really good at dribbling fast, seeing the court, and passing. It is their job to bring the ball down the court and set up offensive plays.
Offensive -- Dribbling, passing, and setting up offensive plays are a guard's main responsibilities. They also need to be able to drive to the basket and to shoot from the perimeter.
Defensive -- On defense, a guard is responsible for stealing passes, contesting shots, preventing drives to the hoop, and for boxing out
.
The Rules
Basketball is a team sport. Two teams of five players each try to score by shooting a ball through a hoop elevated 10 feet above the ground. The game is played on a rectangular floor called the court, and there is a hoop at each end. The court is divided into two main sections by the mid-court line. If the offensive team puts the ball into play behind the mid-court line, it has ten seconds to get the ball over the mid-court line. If it doesn't, then the defense gets the ball. Once the offensive team gets the ball over the mid-court line, it can no longer have possession of the ball in the area in back of the line. If it does, the defense is awarded the ball.
Basketball Court 1
The ball is moved down the court toward the basket by passing or dribbling. The team with the ball is called the offense. The team without the ball is called the defense. They try to steal the ball, contest shots, steal and deflect passes, and garner rebounds.
When a team makes a basket, they score two points and the ball goes to the other team. If a basket, or field goal, is made outside of the three-point arc, then that basket is worth three points. A free throw is worth one point. Free throws are awarded to a team according to some formats involving the number of fouls committed in a half and/or the type of foul committed. Fouling a shooter always results in two or three free throws being awarded the shooter, depending upon where he was when he shot. If he was beyond the three-point line, then he gets three shots. Other types of fouls do not result in free throws being awarded until a certain number have accumulated during a half. Once that number is reached, then the player who was fouled is awarded a '1-and-1' opportunity. If he makes his first free throw, he gets to attempt a second. If he misses the first shot, the ball is live on the rebound.
Each game is divided into sections. All levels have two halves. In college, each half is twenty minutes long. In high school and below, the halves are divided into eight (and sometimes, six) minute quarters. In the pros, quarters are twelve minutes long. There is a gap of several minutes between halves. Gaps between quarters are relatively short. If the score is tied at the end of regulation, then overtime periods of various lengths are played until a winner emerges.
Each team is assigned a basket or goal to defend. This means that the other basket is their scoring basket. At halftime, the teams switch goals. The game begins with one player from either team at center court. A referee will toss the ball up between the two. The player that gets his hands on the ball will tip it to a teammate. This is called a tip-off. In addition to stealing the ball from an opposing player, there are other ways for a team to get the ball.
One such way is if the other team commits a foul or violation.
Fouls and Violations
FOULS
Personal fouls include any type of illegal physical contact.
- Hitting
- Pushing
- Slapping
- Holding
- Illegal pick/screen -- when an offensive player is moving. When an offensive player sticks out a limb and makes physical contact with a defender in an attempt to block the path of the defender.
- Three free throws are awarded if the player is fouled while shooting for a three-point goal and they miss their shot. If a player is fouled while shooting a three-point shot and makes it anyway, he is awarded one free throw. Thus, he could score four points on the play.
- Inbounds. If fouled while not shooting, the ball is given to the team the foul was committed upon. They get the ball at the nearest side or baseline, out of bounds, and have 5 seconds to pass the ball onto the court.
- One & one. If the team committing the foul has seven or more fouls in the game, then the player who was fouled is awarded one free throw. If he makes his first shot, then he is awarded another free throw.
- Ten or more fouls. If the team committing the foul has ten or more fouls, then the fouled player receives two free throws.
Blocking. Blocking is illegal personal contact resulting from a defender not establishing position in time to prevent an opponent's drive to the basket.
Flagrant foul. Violent contact with an opponent. This includes hitting, kicking, and punching. This type of foul results in free throws plus the offense retaining possession of the ball after the free throws.
Intentional foul. When a player makes physical contact with another player with no reasonable effort to steal the ball. It is a judgment call for the officials.
Technical foul. Technical foul. A player or a coach can commit this type of foul. It does not involve player contact or the ball but is instead about the 'manners' of the game. Foul language, obscenity, obscene gestures, and even arguing can be considered a technical foul, as can technical details regarding filling in the scorebook improperly or dunking during warm-ups.
VIOLATIONS
Walking/Traveling. Taking more than 'a step and a half' without dribbling the ball is traveling. Moving your pivot foot once you've stopped dribbling is traveling.
Carrying/palming. When a player dribbles the ball with his hand too far to the side of or, sometimes, even under the ball.
Double Dribble. Dribbling the ball with both hands on the ball at the same time or picking up the dribble and then dribbling again is a double dribble.
Held ball. Occasionally, two or more opposing players will gain possession of the ball at the same time. In order to avoid a prolonged and/or violent tussle, the referee stops the action and awards the ball to one team or the other on a rotating basis.
Goaltending. If a defensive player interferes with a shot while it's on the way down toward the basket, while it's on the way up toward the basket after having touched the backboard, or while it's in the cylinder above the rim, it's goaltending and the shot counts. If committed by an offensive player, it's a violation and the ball is awarded to the opposing team for a throw-in.
Backcourt violation. Once the offense has brought the ball across the mid-court line, they cannot go back across the line during possession. If they do, the ball is awarded to the other team to pass inbounds.
Time restrictions. A player passing the ball inbounds has five seconds to pass the ball. If he does not, then the ball is awarded to the other team. Other time restrictions include the rule that a player cannot have the ball for more than five seconds when being closely guarded and, in some states and levels, shot-clock restrictions requiring a team to attempt a shot within a given time frame.
Player Positions
Center. Centers are generally your tallest players. They generally are positioned near the basket.Offensive -- The center's goal is to get open for a pass and to shoot. They are also responsible for blocking defenders, known as picking or screening, to open other players up for driving to the basket for a goal. Centers are expected to get some offensive rebounds and put-backs.
Defensive -- On defense, the center's main responsibility is to keep opponents from shooting by blocking shots and passes in the key area. They also are expected to get a lot of rebounds because they're taller.
Forward. Your next tallest players will most likely be your forwards. While a forward may be called upon to play under the hoop, they may also be required to operate in the wings and corner areas.
Offensive -- Forwards are responsible to get free for a pass, take outside shots, drive for goals, and rebound.
Defensive -- Responsibilities include preventing drives to the goal and rebounding.
Guard. These are potentially your shortest players and they should be really good at dribbling fast, seeing the court, and passing. It is their job to bring the ball down the court and set up offensive plays.
Offensive -- Dribbling, passing, and setting up offensive plays are a guard's main responsibilities. They also need to be able to drive to the basket and to shoot from the perimeter.
Defensive -- On defense, a guard is responsible for stealing passes, contesting shots, preventing drives to the hoop, and for boxing out
.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)